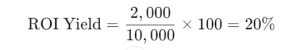The finance landscape in 2025 is more dynamic and data-driven than ever, with businesses and investors relying on specialized knowledge to optimize decision-making. This article explores key financial concepts, offering insights and practical guidance on topics such as revenue’s impact on the balance sheet, cash cycles, dividend calculations, and yield analysis.
How Does Revenue Affect the Balance Sheet?
Revenue, recorded on the income statement, directly impacts the balance sheet by influencing two major areas:
- Assets: Revenue generates cash or accounts receivable, increasing total assets.
- Equity: After expenses, revenue contributes to net income, which is added to retained earnings under shareholder equity.
Example:
- A company earns $100,000 in revenue.
- After expenses, $40,000 remains as net income.
Impact on the Balance Sheet:
- Assets: Cash or accounts receivable increase by $100,000.
- Equity: Retained earnings rise by $40,000 after accounting for costs.
Key Insight:
Revenue growth strengthens a company’s financial position, but excessive liabilities or expenses can negate its positive impact.
What is the Operating Cycle?
The Operating Cycle measures how long it takes a company to convert inventory and other inputs into cash through sales.
Stages of the Operating Cycle:
- Inventory Purchase: Time taken to procure raw materials or stock.
- Sales Process: Period between stocking inventory and selling it to customers.
- Receivables Collection: Time required to collect payment from buyers.
Formula:
Importance:
- A shorter operating cycle enhances liquidity and reduces reliance on external funding.
- An extended cycle may signal inefficiencies in inventory or receivables management.
What is the Formula for Dividend Profit?
Dividend profit refers to the return shareholders earn from dividends distributed by a company.
Formula for Dividend Yield:
Example:
- Annual Dividend Per Share: $2
- Market Price Per Share: $50
Why It Matters:
Dividend yield helps investors assess the return they receive relative to their investment in a stock.
How to Calculate the Cash Cycle?
The Cash Cycle measures the time between cash outflows for inventory purchases and cash inflows from sales.
Formula:
Explanation of Components:
- Inventory Days: Time to convert inventory into sales.
- Receivable Days: Time to collect payments from customers.
- Payable Days: Time taken to pay suppliers.
Example:
- Inventory Days: 60
- Receivable Days: 30
- Payable Days: 45
Why It’s Crucial:
- A shorter cash cycle improves liquidity and reduces financing needs.
- A longer cycle may indicate cash flow issues, requiring corrective action.
What is the Difference Between Yield and Dividend?
Though related, yield and dividend have distinct meanings in finance.
| Aspect | Yield | Dividend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The return on investment expressed as a percentage. | The actual cash payout to shareholders. |
| Formula | Yield=Return/Investment | Calculated as dividend per share. |
| Example | Includes total return (price appreciation + dividends). | Focuses solely on cash dividends paid. |
Use Case:
- Yield is used for comparing investment returns across assets.
- Dividend is relevant for income-focused investors.
What is the Formula for ROI Yield?
Return on Investment (ROI) Yield measures the profitability of an investment as a percentage of its cost.
Formula:
Example:
- Initial Investment: $10,000
- Net Profit: $2,000
Importance:
- Helps investors evaluate the efficiency of their investments.
- A higher ROI indicates better utilization of resources.
Conclusion
Specialized financial topics like cash cycles, operating cycles, and dividend yields are more relevant than ever in 2025. Mastering these concepts allows businesses and investors to navigate complex markets effectively.
By understanding and applying these tools, you can make informed decisions, optimize performance, and ensure long-term success in an ever-evolving financial landscape.
Stay informed, Stay profitable.